Mastering how to meditate with 10 steps to improve breathing offers a meaningful pathway to enhance respiratory health and overall well-being. Incorporating structured meditation techniques into daily routines can lead to profound benefits, including increased relaxation, mental clarity, and better control over breathing patterns. This comprehensive guide explores effective practices rooted in ancient traditions and modern insights, providing a clear roadmap for those seeking to optimize their breath through meditation.
By understanding and applying these carefully designed steps, individuals can cultivate a more mindful approach to breathing, fostering long-term health benefits. From creating an ideal environment to overcoming common challenges, this guide equips you with the necessary tools to establish a sustainable meditation practice focused on improving your respiratory function.
Introduction to Meditation and Breathing Improvement Techniques
Meditation has been practiced for thousands of years across diverse cultures and spiritual traditions as a means to cultivate mental clarity, emotional stability, and physical well-being. Among its various methods, focusing on the breath stands out as one of the most fundamental and accessible practices. Proper breathing techniques not only support meditation but also serve as practical tools to enhance overall health, reduce stress, and promote a balanced state of mind.
Incorporating structured breathing exercises into daily routines can significantly improve respiratory function and foster a deeper sense of mindfulness. By consciously regulating breath patterns, individuals can influence their autonomic nervous system, leading to benefits such as lowered blood pressure, improved oxygen exchange, and increased relaxation. As meditation continues to gain recognition in modern health practices, its emphasis on breath awareness offers a simple yet powerful pathway to improved physical and mental resilience.
Historical and Cultural Contexts of Meditation Focused on Breath
The significance of breath in meditation transcends many ancient civilizations, reflecting a universal understanding of its vital role in human life. In Indian spiritual traditions, particularly within Yoga and Pranayama practices, controlling and expanding the breath has been central to achieving spiritual awakening and physical health for over 3,000 years. Pranayama, meaning “life force extension,” emphasizes specific breathing techniques designed to harmonize body and mind.
Similarly, in Chinese Taoist practices, Qi Gong incorporates mindful breathing to cultivate and balance the body’s vital energy. Buddhist meditation traditions, especially in Zen and Vipassana, utilize breath awareness as an anchor for cultivating mindfulness and moment-to-moment presence. These cultural practices underscore a shared recognition that conscious breathing can serve as a bridge between physical vitality and spiritual development, echoing across history and geography.
Benefits of Integrating Structured Breathing into Daily Routines
Implementing systematic breathing exercises into everyday activities offers a multitude of health and psychological advantages. Consistent practice can improve lung capacity, enhance oxygen delivery to tissues, and support cardiovascular health. Moreover, structured breathing acts as a natural stress relief mechanism, calming the nervous system and reducing the production of stress hormones.
Beyond physical benefits, mindful breathing fosters mental clarity, emotional regulation, and increased focus. For example, individuals experiencing anxiety or high-pressure situations often find that controlled breathing helps them regain composure and clarity. Integrating these techniques into daily routines, such as during morning meditation, commute, or before sleep, can establish a foundation of resilience, promoting long-term well-being and a balanced lifestyle.
Preparing for Meditation

Establishing an optimal environment and mindset before beginning your meditation session is essential for fostering deep relaxation and enhancing focus. Thoughtful preparation not only minimizes distractions but also creates a sanctuary that allows you to fully immerse in your practice, leading to more profound benefits over time.
Effective preparation involves both arranging your physical space and cultivating mental clarity. By intentionally setting the stage and adopting a receptive mindset, you enhance your ability to concentrate and experience tranquility during meditation. This foundational step supports consistency and progress in your mindfulness journey.
Creating a Comfortable, Distraction-Free Meditation Space
To cultivate a conducive environment for meditation, attention should be paid to the physical surroundings. The space should promote comfort and be free from interruptions, noise, and visual clutter. This helps in anchoring your attention inward and establishing a peaceful atmosphere.
- Choose a quiet, private area where external noises are minimized. If absolute silence isn’t achievable, consider using background sounds like gentle nature recordings or white noise to mask disruptive noises.
- Designate a specific spot solely for meditation to reinforce the mental association with relaxation. This could be a corner in your room, a comfy chair, or a dedicated cushion on the floor.
- Ensure proper seating or lying arrangements that support comfort; use cushions or mats to maintain good posture without strain.
- Maintain a clutter-free environment by removing distracting objects such as electronic devices, work materials, or visual disturbances. This helps in cultivating mental clarity.
- Adjust the lighting to be soft and calming, avoiding harsh or bright lights that can hinder relaxation. Natural light or dim lamps are ideal choices.
Creating an ambiance that evokes tranquility involves considering sensory elements beyond sight, such as using calming scents like lavender or chamomile through diffusers, and maintaining a comfortable room temperature to prevent discomfort.
Fostering a Focused and Relaxed Mindset
Before starting your meditation, it is crucial to prepare your mind to foster focus and relaxation. This mental readiness involves intentional practices that clear mental clutter and set a positive tone for your session.
- Practice a few minutes of gentle breathing exercises to shift your focus from external worries to your internal experience. Deep, slow breaths help calm the nervous system and create a receptive state.
- Engage in mindfulness or a brief body scan to become aware of physical sensations and release tension. Noticing areas of tightness enables you to consciously relax those muscles.
- Set a clear intention or acknowledge your purpose for meditating. For example, you might focus on cultivating compassion, patience, or simply being present.
- Avoid rushing into meditation immediately after stressful activities. Instead, take a moment to pause, breathe, and transition into a calm mindset.
- Adopt a gentle, non-judgmental attitude towards your practice, embracing wherever your mind may wander without frustration. This cultivates patience and persistence.
“A calm mind is the foundation of a profound meditation experience. Preparing mentally allows you to approach your session with openness and clarity.”
Incorporating these steps into your pre-meditation routine can dramatically improve your focus, deepen relaxation, and enhance the overall effectiveness of your practice. Consistent mental and environmental preparation creates a supportive space for mindfulness to flourish and leads to lasting benefits in your well-being.
Step-by-Step Guide to the 10 Meditation Practices for Better Breathing
Enhancing breathing through meditation involves a series of structured practices designed to cultivate awareness, deepen diaphragmatic engagement, and promote relaxation. This guide provides ten detailed meditation practices that can be incorporated into daily routines to improve respiratory health, reduce stress, and foster overall well-being.
Each practice targets specific aspects of breath control and mindfulness, enabling practitioners to develop a more conscious and efficient breathing pattern. Regular application of these techniques can lead to increased lung capacity, reduced anxiety levels, and a more balanced nervous system.
Breath Awareness Exercises
Breath awareness serves as the foundation of effective meditation, encouraging mindfulness of the natural flow of breath without interference.
| Technique | Purpose | Duration | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Natural Breath Observation | Develops present-moment awareness and resets the mind to focus solely on breathing patterns. | 5-10 minutes | sit comfortably, close eyes, and simply observe each inhale and exhale without trying to modify it. |
| Counting Breaths | Enhances concentration and stabilizes attention during meditation. | 5-7 minutes | inhale for a count of four, exhale for a count of four, gradually increasing counts as comfort allows. |
Focusing on the breath as it naturally flows allows the practitioner to anchor attention, reducing mental chatter and promoting calmness.
Deep Diaphragmatic Breathing
This practice emphasizes engaging the diaphragm to maximize oxygen intake and strengthen respiratory muscles.
| Technique | Purpose | Duration | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diaphragmatic Expansion | Increases lung capacity and promotes efficient oxygen exchange. | 10 minutes | lie flat or sit upright, place one hand on your chest and the other on your abdomen, breathe deeply through the nose, feeling the abdomen rise. |
| Slow Deep Breaths | Reduces stress and encourages relaxation of the nervous system. | 10 minutes | inhale slowly through the nose for a count of six, hold briefly, then exhale fully through pursed lips for a count of six. |
Consistent diaphragmatic breathing enhances respiratory efficiency and fosters a sense of tranquility.
Alternate Nostril Breathing Techniques
This pranayama method balances the autonomic nervous system and promotes mental clarity.
| Technique | Purpose | Duration | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nadi Shodhana (Alternate Nostril Breathing) | Harmonizes hemispheric activity and alleviates stress. | 5-10 minutes | Using the thumb to close the right nostril, inhale through the left; then close the left nostril, exhale through the right; continue alternating sides smoothly. |
| Cooling Breath | Calms hyperactivity and improves breath regulation. | 5 minutes | inhale through one nostril, hold briefly, then exhale through the other; repeat while maintaining gentle control. |
This technique enhances nasal airflow, balances energy, and fosters mental steadiness.
Guided Visualization Focusing on Breath Flow
Visualization aligns the mind with the breath, creating a calming narrative that fosters greater control and awareness.
| Technique | Purpose | Duration | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flow of Breath Visualization | Strengthens the connection between mind and body, promoting relaxation. | 10 minutes | Close eyes and imagine the breath as a flowing stream, visualizing each inhale as a gentle wave entering the body and each exhale as a calm wave leaving. |
| Light and Breath Integration | Enhances mindfulness and visual focus during breathing | 8-10 minutes | Visualize a soft, glowing light entering with each inhale, filling the lungs and body, then slowly radiating outward on each exhale. |
Guided imagery transforms breathing into a soothing, vivid experience that deepens meditative states.
Progressive Muscle Relaxation Combined with Breath Control
This practice combines muscle relaxation techniques with breath work to release tension systematically across the body.
| Technique | Purpose | Duration | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Body Scan with Breath Focus | Reduces physical and mental tension, improves breath quality. | 15 minutes | Start at the toes, tense muscles as you inhale, then relax fully with each exhale, moving upward through the body regions. |
| Muscle Tension Release | Creates a state of physical ease, facilitating deeper breathing. | 10-12 minutes | contract muscle groups for 5 seconds during inhalation, then release abruptly on exhalation, paying attention to the sensations of relaxation. |
Integrating muscle relaxation with breath control enhances overall meditative depth and physical comfort.
Techniques to Enhance Breathing During Meditation
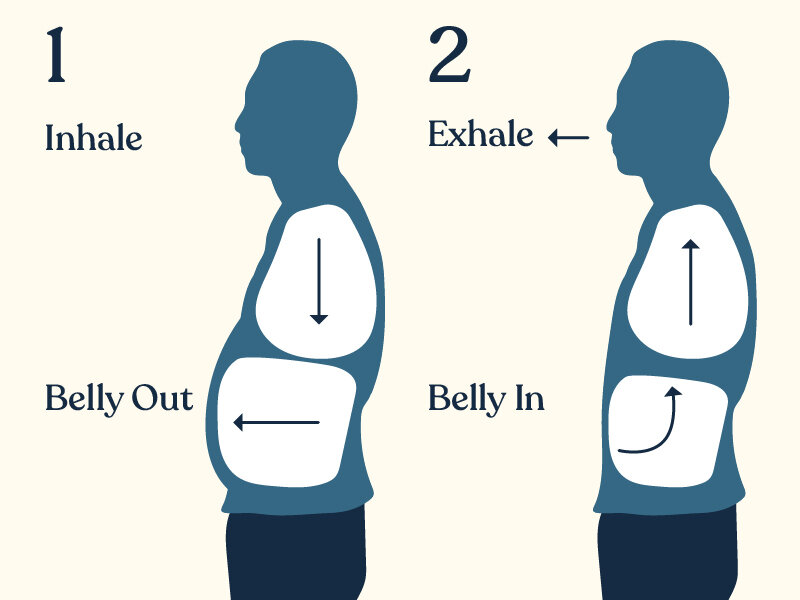
Optimizing breathing techniques during meditation can significantly deepen relaxation, improve respiratory efficiency, and foster a greater sense of mindfulness. Employing specific methods such as slow breathing, rhythmic patterns, and breath counting helps practitioners develop greater awareness of their breath, leading to enhanced physiological and mental benefits. Integrating these techniques into your meditation practice can transform your experience, making it more restorative and sustainable over time.
These methods influence respiratory health by promoting diaphragmatic breathing, reducing unnecessary muscle tension, and encouraging a balanced oxygen-carbon dioxide exchange. Consistent use of such techniques can help alleviate stress, lower blood pressure, enhance lung capacity, and improve overall respiratory function. Below are detailed approaches to refine breathing during meditation practice.
Slow Breathing and Rhythmic Patterns
Slow and rhythmic breathing techniques involve consciously regulating the pace and pattern of your breath. These methods help calm the nervous system, reduce heart rate, and promote a state of tranquility. Practitioners often find that slowing down their breath to a comfortable rhythm facilitates deeper meditation and can have lasting benefits for respiratory health.
To implement these techniques, begin by consciously inhaling and exhaling at a controlled pace, focusing on maintaining smooth, even breaths. Rhythmic patterns introduce specific timing ratios, which can help synchronize breathing with bodily movements or sounds, further enhancing mindfulness and physiological harmony.
Breath Counting and Synchronization
Breath counting involves silently keeping track of each inhalation and exhalation cycle, which cultivates concentration and prevents the mind from wandering. Synchronizing breath with body movements—such as gentle nodding or hand gestures—or with vocal sounds like mantras, can deepen the meditative state by integrating breath awareness with physical or auditory cues.
These techniques promote a harmonious connection between breath and body, encouraging a more effortless and natural breathing pattern that supports respiratory efficiency. Regular practice can lead to improved lung capacity, better oxygenation, and a reduction in respiratory fatigue or discomfort.
Breathing Ratios and Patterns
Understanding and applying specific breathing ratios can optimize oxygen intake and carbon dioxide expulsion, contributing to better respiratory health. Different ratios serve various purposes, from relaxation to energization, depending on the meditation goal.
| Pattern Name | Inhalation | Exhalation | Ratio Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Box Breathing | 4 seconds | 4 seconds | Equal inhalation and exhalation, held pause in between |
| 4-7-8 Breathing | 4 seconds | 8 seconds | Inhale for 4 seconds, hold for 7 seconds, exhale for 8 seconds |
| Diaphragmatic Breathing | 6 seconds | 6 seconds | Deep belly breath focusing on diaphragmatic expansion and contraction |
| Alternate Nostril Breathing | Variable (typically 4 seconds) | Variable (typically 4 seconds) | Alternating nostrils to balance both hemispheres of the brain and respiratory pathways |
Slow, rhythmic, and patterned breathing techniques facilitate parasympathetic nervous system activation, which promotes relaxation, lowers blood pressure, and enhances respiratory efficiency.
Physiologically, these practices improve alveolar ventilation, optimize gas exchange, and support the regulation of respiratory muscles. Regularly engaging in such techniques helps strengthen lung function, reduce anxiety-induced hyperventilation, and cultivate a resilient respiratory system capable of supporting sustained meditation practices.
Common Challenges and Solutions in Meditation for Breathing Improvement

Meditation for breathing enhancement can be highly beneficial, yet practitioners often encounter obstacles that hinder progress. Recognizing these common challenges and implementing effective strategies can significantly improve the meditation experience and outcomes. Overcoming distractions, managing physical discomfort, and adapting techniques to individual needs are essential steps toward maintaining consistency and achieving the desired benefits from your practice. During meditation, it is normal to face certain difficulties.
These challenges may stem from mental, physical, or environmental factors that interfere with focus and relaxation. Understanding how to address them effectively ensures that meditation remains a sustainable and rewarding activity, ultimately leading to better breathing and overall well-being.
Addressing Restless Thoughts and Mental Distractions
Mental chatter and restless thoughts are among the most prevalent obstacles faced during meditation. These distractions can divert attention from breathing exercises, making it difficult to achieve a state of calm. To counteract this, practitioners should acknowledge these thoughts without judgment and gently redirect focus back to the breath. Techniques such as labeling thoughts as “thinking” and returning attention to inhalation and exhalation help cultivate mindfulness and reduce mental noise over time.
Managing Shallow or Irregular Breathing
Shallow breathing often results from anxiety or improper technique, limiting the benefits of meditation. When experiencing shallow breaths, it is helpful to consciously slow down and deepen each inhalation and exhalation, ensuring the breath reaches the diaphragm. Incorporating slower, more deliberate breathing patterns during meditation can train the body to adopt more efficient breathing habits, which are crucial for improving lung capacity and oxygen intake.
Adjusting Techniques to Suit Individual Needs
Every practitioner has unique physical and mental conditions that influence how meditation should be approached. Customizing breathing exercises—such as altering breath length, posture, or location—can make practices more accessible and comfortable. For example, individuals with respiratory issues might prefer gentle, shorter sessions, while those seeking deeper relaxation may opt for longer, more diaphragmatic breaths. Listening to one’s body and making incremental adjustments fosters sustainable progress.
Troubleshooting Tips for Common Challenges
To assist practitioners in overcoming typical meditation hurdles, the following quick-reference tips are recommended:
- Persistent mental distraction: Use a simple mantra or focus word to anchor your attention when the mind wanders.
- Shallow breathing: Incorporate diaphragmatic breathing exercises outside of meditation sessions to develop deeper, more effective breaths.
- Physical discomfort or stiffness: Adjust your posture gradually; use cushions or supports to maintain comfort and avoid strain.
- External noise or environmental interruptions: Choose a quiet, dedicated space for meditation, or use soothing background sounds, such as white noise or nature recordings, to mask disruptions.
- Feeling impatient or frustrated: Practice patience and gentle self-compassion, recognizing that progress in meditation is gradual and non-linear.
By proactively addressing these challenges with patience and tailored strategies, practitioners can enhance their meditation experience and improve their breathing over time. Consistent practice, combined with adaptability, creates a resilient foundation for cultivating mindfulness and respiratory health.
Incorporating Meditation into Daily Life for Long-term Benefits

Maintaining a consistent meditation practice that emphasizes breathing improvement can significantly enhance overall well-being and resilience to stress. Integrating meditation seamlessly into daily routines ensures sustainability and ongoing benefits, fostering a healthier lifestyle over time. Establishing simple, achievable habits allows individuals to experience the cumulative advantages of improved breathing, mental clarity, and emotional balance.Embedding meditation into everyday activities transforms it from a task into a natural part of life.
By creating dedicated times for practice and adjusting techniques to fit personal schedules, individuals can sustain their commitment without feeling overwhelmed. Tracking progress and refining techniques over time serve as motivation and ensure continuous development in breathing health. This strategic approach facilitates long-term engagement and the development of healthier respiratory and mental habits.
Establishing Consistent Daily Routines
Integrating meditation into daily life involves creating structured yet flexible routines that suit individual schedules. Consistency is key to reaping long-term benefits, and this can be achieved through:
- Designating specific times each day, such as morning upon waking or before bedtime, to establish a routine.
- Starting with brief sessions, such as five to ten minutes, and gradually increasing duration as comfort and familiarity grow.
- Incorporating meditation into existing daily activities, like practicing mindful breathing during commutes, breaks, or household chores.
- Utilizing reminders or alarms to prompt regular practice, ensuring it becomes a non-negotiable part of the day.
Consistency in practice not only enhances breathing efficiency but also cultivates mental discipline, making meditation an integral component of personal health management.
Tracking Progress and Adapting Techniques
Regular monitoring of meditation outcomes enables individuals to recognize improvements and make necessary adjustments for sustained growth. Effective methods include:
- Maintaining a meditation journal to record session durations, breathing sensations, emotional states, and overall feelings after each practice.
- Using mobile applications that offer guided sessions, breathing exercises, and progress tracking features to facilitate accountability.
- Reviewing journal entries weekly to identify patterns, challenges, and areas needing focus or variation.
- Adjusting the meditation techniques over time, such as incorporating different breathing patterns or mindfulness strategies, based on personal feedback and progress.
“Progress is a journey, not a destination. Celebrate your small victories in breathing and mindfulness each day.”
Flexibility in technique adaptation allows for overcoming plateaus, preventing stagnation, and maintaining motivation. Recognizing and celebrating incremental improvements encourages continued commitment and deepens the benefits of meditation.
Sample Weekly Meditation Plans for Sustained Improvement
Designing varied weekly schedules ensures engagement and addresses different aspects of breathing and mental health. Below is a sample plan that balances foundational practices with advanced techniques:
| Day | Meditation Focus | Practice Duration | Additional Techniques |
|---|---|---|---|
| Monday | Basic diaphragmatic breathing | 10 minutes | Body scan for relaxation |
| Tuesday | Box breathing (inhale-hold-exhale-hold) | 12 minutes | Progressive muscle relaxation |
| Wednesday | Mindfulness breathing with visualization | 10 minutes | Guided imagery to enhance lung capacity |
| Thursday | Alternate nostril breathing | 8 minutes | Focus on balancing energies |
| Friday | Breath counting meditation | 10 minutes | Focus on breath retention |
| Saturday | Extended deep breathing session | 15 minutes | Gentle stretching beforehand for openness |
| Sunday | Reflection and gratitude breathing | 10 minutes | Affirmations supporting respiratory health |
This varied approach encourages continuous engagement, challenges different breathing patterns, and fosters long-term adaptation to maintain respiratory health and mental clarity.
Final Review

Incorporating these 10 meditation steps into your daily life can lead to lasting improvements in your breathing and overall mental health. Consistency and mindfulness are key to experiencing the full spectrum of benefits, from reduced stress to enhanced physical well-being. As you continue this practice, you’ll discover a calmer, more balanced way to navigate life’s challenges with every mindful breath you take.